Mountains and Plateaus
by Devender
0 2186
Mountains and Plateaus
- Mountains:
- Fold Mountains
- Block Mountains
- Volcanic Mountains
- Residual/Dissected/Relict Mountains
- These mountains are closely associated with volcanic activities
- It contains a lot of active volcanoes especially in circum Pacific fold mountain system
- These mountains are rich in minerals such as Tin, Copper, Gold & Petroleum
- This faulting results in the formation of Block Mountains & their counterparts in rift valleys
- Tension is the cause behind the formation of these large scale black mountains and rift valleys, not compression
- These mountains are very common in the circum pacific belt
- Plateaus:
- Tectonic Plateaus
- Volcanic Plateau
- Dissect Plateaus
- When these plateaus are surrounded by mountains they are known as inter-montane plateaus. For example - Tibetian plateau, Bolivian Plateau
- When the plateaus are surrounded by the sea or plains, they are known as Continental Plateaus. For example - Deccan plateau, Greenland plateau, South Africa plateau
- The high plateaus wore down & their surface becomes irregular
- African plateau yields gold, diamonds, copper, Manganese & Chromium
- Brazilian plateau yields iron & Manganese
- Deccan Plateau Yields Manganese, Iron & Coal
- Western Australian plateau yields Gold & Iron
Mountains are part of the land having a height of over 900 meters and a slope of around 25 to 30*. There are mainly 4 types of mountains namely:
1 Fold Mountains:
These are formed by the folding of geosyncline sediments under compressible tectonic forces. Fold Mountains are also called mountains of elevation as the rock strata have been elevated to great heights.
For example - Himalaya, Alps, Rockies, Andes, Alapchhian, Ural, Aravalis
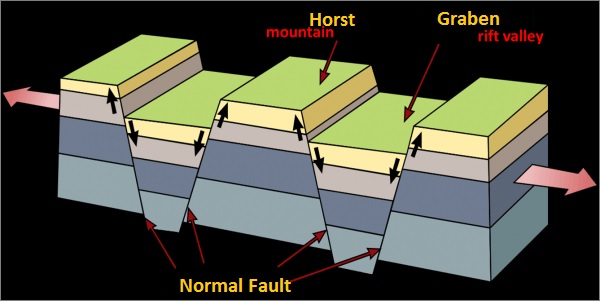
2 Block Mountains:
These mountains are formed by faults that are caused by tension or compression forces that lengthen or shorten the earth's crust. It causes a section of it to subside or rise above the surrounding level.
For example - Vosges (France), Black Forest (Germany)
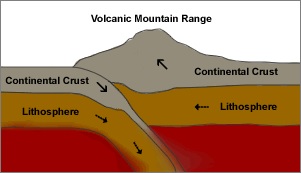
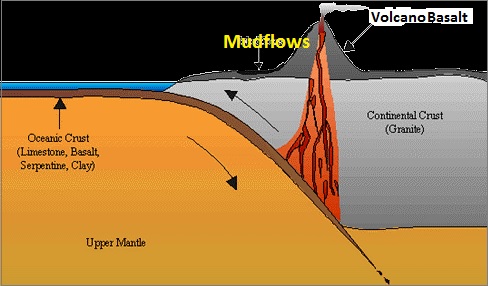
3 Volcanic Mountains:
These mountains are also known as mountains of accumulation and are formed due to the accumulation of thick lava that came from volcanic eruptions.
For example - Fuji Yama (Japan), Mt. Popa (Myanmar), Mt. Mauna loa (Hawai), Mt. Mayon (Philippines), Mt. Agung (Bali), Mt. Merapi (Sumatra) & Mt. Catopaxi (Ecuador)
4 Residual/Dissected/Relict Mountains:
These mountains are formed due to the waning of previously existing elevated regions by erosion. These are also known as the mountains of denudation as these are evolved by denudation where the general level of land got lowered due to agents of denudation.
For example - Nilgiris, Parshavnath, Hills of Peninsula India, Mt. Manodnock (USA)
Plateaus are elevated areas compared to their surroundings that have a large almost flat top area. They are also known as tableland. Their original characteristics are highly altered as they are subjected to erosional processes.
The plateaus can be divided into 3 categories based on their mode of formation & their physical appearance which are:
1 Tectonic Plateau:
These are formed by earth movements that cause uplift of considerable size with fairly uniform altitude.
For example - Deccan plateaus, Mesera plateau (tilted of central Iberia) & Harz plateau (Faulted of Germany)
2 Volcanic Plateaus:
The molten lava from the volcanic eruptions solidifies to form successive sheets of basaltic lava. It is known as the Lava plateau.
For example - Antrim Plateau of Northern island, NW part of Deccan Plateau & Columbia Snake Plateau (Biggest one)
3 Dissect Plateaus:
These are formed by continuous weathering & erosion by running water, wind & ice.
For example - Scottish Highland
The Plateaus are known for their rich mineral resources & have been actively mined. For example: -

Share:




Comments
Waiting for your comments