Igneous Rocks, Sedimentary Rocks, Metamorphic Rocks
by Devender
0 2674
These three rocks forms the crust of the earth's surface.
Igneous Rocks, Sedimentary Rocks, Metamorphic Rocks
The earth's crust consists of rocks that form this upper layer. These rocks can be divided into three parts.

- Igneous Rocks:
- Basic rocks have a high proportion of basic oxides mainly of iron, aluminum & magnesium
- Acidic rocks contain a high proportion of silica and are less dense & lighter in color
- Igneous rocks are known as parent or primary rocks as all other rocks are derived from them.
- Plutonic Rocks
- Volcanic Rocks
- For example - Granite, Diorite & Gabbro
- For example - Basalt
- Sedimentary Rocks:
- Sediment is deposited layer by layer in form of strata hence also known as stratified rocks
- The process of turning sediments into hard rock layers by pressure is known as lithification
- These rocks are non-crystalline & often contains fossils of animals, plants & other microorganisms
- Mechanically formed
- Organically formed
- Chemically formed
- Metamorphic Rocks:
- Granite to Gneiss
- Mica to Schist
- Gabro to Serpentite
- Limestone to Marble
- Sandstone to Quartzite
- Shale to Schist
- Coal to Graphite
- Bituminous coal to Anthracite coal
These rocks are formed by cooling and solidification of molten material magma that erupts from volcanoes. It moves towards the earth's surface through the crack. It is crystalline in structure, does not occur in strata & does not contain fossils. It can be further divided into 2 groups on the basis of mineral composition.
These rocks are mainly hard and resistant so they are used for constructing roads. These rocks are also polished as monuments & gravestones.
The Igneous rocks can be categorized into 2 categories based on the terms of origin which are:
The Plutonic rocks are formed due to the solidification of magma. These are cooled and solidified slowly so that large, easily recognized crystals are formed till some depth inside the earth's crust. These get exposed to the surface because of denudation & erosion.
The volcanic rocks are formed due to the solidification of lava. Lava is molten rocks poured out of volcanoes. They have solidified rapidly on the earth’s surface due to which it has small crystals.
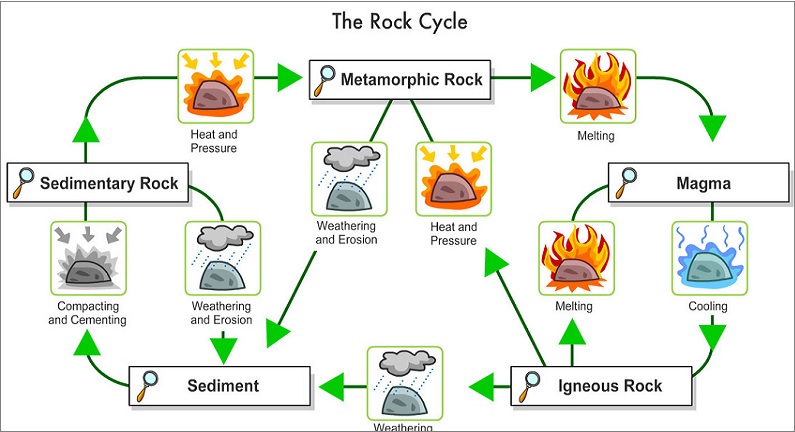
These are formed due to the deposition of layers of sediment along with the water bodies over a long period of time. These rocks may be fine-grained or coarse, soft or hard & the material forming them may be brought by streams, glaciers, winds, or even animals.
The sedimentary rocks are may be derived from Igneous, Metamorphic or Sedimentary rocks that is why they are considered most varied in the formation of all rocks.
These rocks can be classified into 3 categories according to their origin & composition that are:
The mechanically formed rocks are formed from the accumulation of materials derived from other rocks. These are made from sand grains with tremendously varying texture, composition & color and are mainly used for building purposes or for making grindstones. Sand & gravel may occur in uncemented form.
The organically formed rocks are formed from the remains of living organisms such as corals or shellfish, whose fleshy part has been decomposed, leaving behind the hard cells. The most common rocks formed by this process are the Calcareous type. For example - Limestone & Chalk. Carbonaceous rocks are also organically formed but from vegetative matter. The pressure of overlying sediments has compressed the plant's remains into compact masses of carbon which eventually becomes Peat, Lignite, or Coal.
The Chemically formed rocks are formed chemically from solutions of one another. For example - Gypsum (Calcium sulfate) is obtained from the evaporation of salt lakes having high salinity. Potash & Nitrates may be formed in the same way.
These rocks are formed when the original structure of igneous & sedimentary rocks partially or wholly change under the action of heat & pressure. It doesn't have any fossils and stratification. For example - The transformation of Clay to Slate.
Transformation of Igneous rocks to Metamorphic rocks
Transformation of Sedimentary rocks to Metamorphic rocks

Share:





Comments
Waiting for your comments