Atmosphere – Weather and Climate
by Devender
0 2614
Atmosphere - Weather and Climate
Weather: It is the condition of the atmosphere at a given place at a specific time.
Climate: It is the average condition of whether at a given place over a period of time like 30-35 years.
- The climate of the temperate latitudes changes more often than that of tropics
- The climate of Britain is so changeable that many people say about it "Britain has no climate, it only has weather"
- The climate of Egypt is so static that people say, "Egypt has no weather but the only climate"
- Death rates are high in tropical areas compared to desert areas because germs don't transmit in high heat and low humidity regions
- The difference in climate and weather all over the world is because of the variable water content in the atmosphere
- Rainfall:
- To find the annual rainfall, rainfall of every month is added
- The mean annual rainfall is obtained by the average of annual rainfall over a long period of time like 30-35 years
- Places having the same mean annual rainfall are joined by a line over a map which is known as isohyet
- Pressure:
- Places with equal pressure are joined by lines on a map known as isobars
- Pressure reading at different places differ due to a number of factors such as Altitude, Gravitational forces, temperature, and sensitivity of mercury
- A mercury barometer that dips in liquid mercury is not okay for outdoor measurements
- A more probable but less accurate type known as the aneroid barometer is used
- A modified type of aneroid barometer known as altimeter is used in Airplanes
- For a continuous record of pressure changes, a self-recording barogram is used
- Temperature:
- The temperature that we use is known as shade temperature that is the temperature of the air
- Precautions need to be taken to exclude the intensity of the sun's radiant heat
- It is done by placing thermometers in a standard meteorological shelter known as Stevenson screen
- Lines joining the places with equal temperature in the map are known as isotherms
- It influences the water vapor in the air and thus decides how much moisture can air hold
- It also governs the rate of evaporation and condensation
- It affects the nature & types of cloud formation & precipitation as relative humidity is directly related to the temperature of the air
- Winds:
- Sunshine:
- Clouds:
- The amount of cloud cover is expressed in eighths or Oktas, for example, 4/8 is half covered & 8/8 is complete overcast
- The lines joining the places with an equal degree of cloudiness is known as isonephs
- Haze:
- Merits of Koeppen's Scheme of classification:
- It uses a shorthand code of letters for the climatic types, so that repetition of descriptive terms becomes unnecessary
- All the major climate groups, sub-groups, and further subdivisions are described by a combination of letters
- It is so simple and detailed that it can be easily used at different educational levels
- Demerits of Koeppen's Scheme of classification:
- It provides international shorthand describing climatic regions that are rather difficult to characterize in words
- It is empirical and, therefore, is based on facts and observations
- It can't measure precipitation accurately
Elements of Weather & Climate
It is measured by the Rain gauge and an inch of rainfall means the amount of water that would cover the ground to a depth of 1 inch, given that none is evaporated. A daily record of rainfall is added to find the total rainfall of the month at the end of the month.
It is measured by the barometer which was invented by Galileo and Torricelli. Air is made up of different gases and it has mass. So, it exerts pressure on the earth's surface which differs from place to place and time to time.
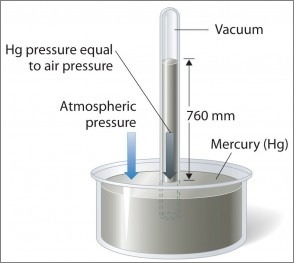
The variation in the atmospheric pressure on the mercury surface is balanced by a column of mercury in a glass tube. However, any liquid could be used for this purpose. Mercury is used because it is the heaviest known liquid.
It is measured by a thermometer which is a narrow glass tube filled with mercury or alcohol. The temperature measured in open daylight is very high as it measures direct insolation from the sun. It is better known as the temperature in the sun which is mainly used for measuring temperature for agricultural purposes.
The temperature plays an important role which is as follows:
The instrument that is used to measure the wind direction is the wind vane or weather clock. The speed of wind is measured by an anemometer.

Sunshine duration is recorded by a sundial in the meteorological station. The line joining the places with equal sunshine duration is known as isohels.
When air rises, it is cooled down by expansion and after reaching the dew point, cooling leads to condensation of water vapor in the atmosphere. The tiny water droplets which are too small to fall as rain or snow get suspended in the air & float as clouds.
Haze is used in connection to the reduction of visibility in regions of low humidity. It is caused by smoke & dust particles in industrial areas or by unequal refraction of light in the air of different densities in the lower atmosphere.
Koeppen's Scheme of Climate classification
Koeppen reorganized a closed relationship between vegetation & climate and he based his classification on the amount of precipitation & temperature.
| Tropical | A | The average temperature of the coldest month is greater than or equal to 18 Degree C |
| Dry Climates | B | Evaporation is greater than Precipitation |
| Warm Temperate | C | Avg. temperature of coldest month 18 Degree C > x > 3 Degree C (mid latitudes) |
| Cold snow forest climate | D | Avg. temp. of coldest month is less than or equal to 3 Degree C |
| Cold Climates | E | Avg temp. of all months is less than 10 Degree C |
| High Land Climate | H | Cold due to elevation |
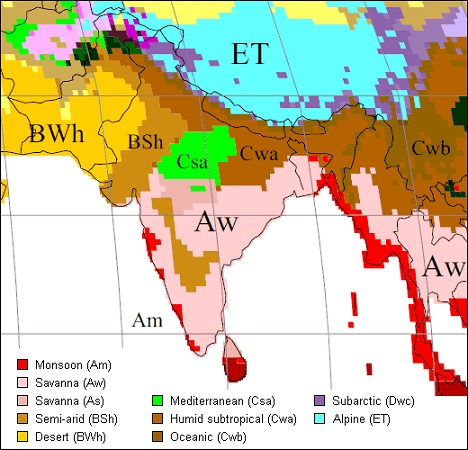
| Amw | Monsoon with a short dry season | West Coast below Goa |
| As | Monsoon with dry summer | East Coast Tamilnadu |
| Aw | Tropical Savanna | Most of the Peninsular plateaus, south of the Tropic of Cancer |
| Bshw | Semi-arid steppe climate | North-western Gujarat, some parts of western Rajasthan and Punjab |
| Bwhw | Hot desert | Extreme western Rajasthan |
| Cwg | Monsoon with dry winter | Ganga plain, eastern Rajasthan, northern Madhya Pradesh, most of North-east India |
| Dfc | Cold humid winter with short summer | Arunachal Pradesh |
| E | Polar type | Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, and Uttarakhand |
He divided the earth into 5 major climatic groups out of which 4 are based on temperature and 1 on precipitation along with the cold climate of high lands. This system recognizes five major climatic types which are designated by a capital letter.
It is more appealing to geographers because of the visible association of vegetation with climatic types. This system of climatic classification is descriptive and generalized.
One of the major setbacks is it is based on the mean monthly values of temperature and precipitation.
Thornthwaite Scheme of Climate classification
It is mainly based on the concept of water balance which is the rate of precipitation – the rate of evaporation.
According to it, an area is arid if there is water deficiency in all months and it is humid if it has water surplus in all months.

Share:




Comments
Waiting for your comments