Mughal Empire
by Devender
0 2856
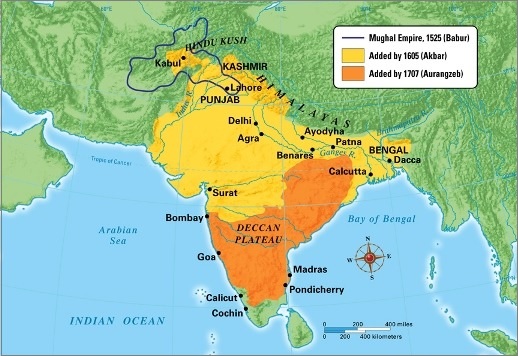
After the end of the Delhi Sultanate, India witnessed the rule of the Mughal Empire. It started after Ibrahim Lodi lost the First battle of Panipat in 1526 to Babur.

Mughal Empire
- Babur:
- Humayun:
- Battle of Chausa:
- Battle of Kannauj or Bilgram:
He ruled from 1526 to 1530. He fought the first battle of Panipat in 1526 against Lodi in which he killed Lodi and captured Delhi. After that he claimed himself to be the "Emperor of Hindustan".
Babur sent his son Humayun to occupy Agra and the Battle of Khanua happened in 1527 near Agra. Babur was against Rana Sanga of Mewar in which Babur again won and assumed the title of Ghazi. He wrote about his life in the book "Tuzuk–i–Baburi" in Turki language. Babur died in 1530.
He was the eldest son of Babur and he ruled from 1530 to 1540. His name meant lucky but he was the unluckiest Mughal ruler. He gave his 3 brothers places to rule. He gave Kabul & Kandhar to Kamran, Sambhal to Aksari & Alwar to Hindal.
When he was busy fighting the Afghans (Shar khan/Sher shah), he received the news that Bahadur shah of Gujarat is advancing on Delhi so he made a treaty with Sher shah. Humayun then captured Gujarat from Bahadur shah and made his brother, Aksari its governor. However, soon Bahadur shah reclaimed Gujrat from Aksari who fled from there.
It happened in 1539 where Sher Shah and Humayun fought against each other. Sher Shah destroyed the Mughal army and Humayun fled from there.
It happened in 1540 between Humayun and Sher shah again. This time, Babur didn't get the support of his brothers and he had to fight alone. He was totally defeated by Sher shah this time and he got exile for 15 years after this war.
Sur interregnum
After defeating Humayun, Sher Shah became the ruler of Delhi in 1540 and he ruled from 1540 to 1555. He formed 4 ministries for central administration namely:
- Diwan–i–Wazirat: Headed by Wazir who was in charge of finance & revenue
- Diwan–i–Ariz: Headed by Military Incharge
- Diwan–i–Rasalat: Headed by Foreign minister
- Diwan–i–Insha: Headed by Communication minister
- Administration:
- Architecture:
Sher shah divided his empire into 47 Sarkars with Chief Shiqdar to maintain law & order in each sarkar and Chief Munsif as Judge in each Sarkar. Each sarker was further divided into Parganas with each pragana having its own Military officer known as Shiqdars, Land revenue officer known as Amin, Treasurer known as Fotedar, and Accountant known as Karkuns.
He introduced new silver coins which were known as Dam. These coins were in circulation till 1835. He laid the foundation for 4 important highways and built rest houses along each one. These highways are Sonargaon to Sind, Agra to Burhampur, Jodhpur to Chittor, and Lahore to Multan.
He also built a new city on the river Yamuna banks near Delhi. He built Mausoleum at Sasaram which is still considered one of the finest pieces of Indian Architecture. He patronized Malik Muhammad Jayasi who wrote the famous Hindi work Padmavat during his reign.
Mughal Empire
- Humayun:
- Akbar:
- Akbar's Religious Touch:
- Akbar's Land Revenue system:
- Akbar's Mansabdari system:
- Jahangir:
- Shahjahan:
- Aurangzeb:
- Aurangzeb's Religious Policies:
- Architecture under Mughals:
- Painting and Music:
- Literature:
- Trivia:
Humayan was able to defeat Afghans in 1555 and reclaimed Delhi. He died in 1556 after falling from the staircase of his library.
Akbar ruled from 1556 to 1605 but during his first Five years of reign, Bairam khan acted as his regent and consolidated the Mughal empire. The second battle of Panipat happened between Akbar and Hemu who was commander of Afghans in 1556. Akbar emerged victorious in this battle with the help of Bairam khan.
Akbar married Rajput princess Jodha who was the daughter of Raja Bhairomal of Amber due to which Mughals got the support of Rajputs. This marriage became a turning point for Mughals as Rajputs now started supporting Mughals. Akbar gave many Rajputs like Raja Man Singh & Raja Bhagwan Das senior positions in his court.
The Battle of Haldighati happened in 1576 between Akbar and Maharana Partap of Mewar. Mughal army was under the leadership of Raja Man Singh and they were able to defeat Rana Partap.
Akbar was very tolerant toward all religions. He abolished the pilgrim tax and later Jiziya. He also formed a strong alliance between the Mughals and Rajputs which provided stability in Northern India and Rajasthan.
He had early contact with Sufi Saints and received teachings from his teacher Abdul Latif. He abolished pilgrimage tax & Jiziga after marrying Jodha Bai and he allowed her to worship her Hindu gods. He had associations with intellectual giants like Shaikh Mubarak & his 2 sons – Abul Faizi & Abul Fazal.
He was a pious Muslim in his early life but later became a skeptic one. He constructed Ibadat khana at his new capital Fatehpur Sikri. He used to invite scholars from all religions to discuss religious policies. He even didn't like the interference of Muslim Ulemas in political matters.
He issued an infallibility decree and asserted his religious powers in 1579 and in 1582, he started a new religion "Din–i–Ilahi" or divine faith in one god. It contained good points of all the religions and uphold no dogma. It mainly aimed to bridge the gap b/w all religions however only 15 people joined this religion.
His land revenue system was known as Zabti/Bandobast system. It was further modified by Raja Todarmal and called the Dahsala system which had: Measurement of land, Revenue based on an average yield of last 10 years, and lands were 4 categories. These categories were: Polaj - cultivated every year, Parauti - cultivated in 2 years, Chachar - cultivated in 3-4 years and Banjar - which was cultivated in 5 years.
Under this system, every officer was given a rank known as Mansab where the lowest officer got 10 coins whereas the highest officer got 5000 coins for their services. It includes all public services except Judiciary. The ranks were also divided into two categories namely: Zat and Sawar. Zat Described the personal status of a person whereas Sawar meant the Number of cavalrymen a person is required to maintain.
After the death of Akbar, prince Salim succeeded the throne with the name of Jhangir which meant conqueror of the world. He witnessed rebellion from his own son Khusaro but managed to defeat & imprison him. He also beheaded the fifth Sikh Guru Arjun dev. He married Mehrunnisa in 1611 and wrote his biography named Tuzuk–i–Jahagiri.
He married Mumtaj and conquered Deccan (Bijapur & Golkunda). He put these under the leadership of his son, Aurangzeb. Later, Aurangzeb killed his 3 brothers and imprisoned Shahjahan in female quarters at Agra fort. Although, Aurangzeb never ill-treated Shahjahan.
He ruled from 1658 to 1707 and assumed the title of Alamgir which meant world conqueror. He attacked Golkunda & Bijapur to contain the Marathas (Shivaji). He defeated the Marathas but it removed the only boundary between Marathas and Mughals. According to JN Sarkar, Deccan ulcer ruined Aurangzeb.
He was very orthodox and staunch Muslim. He even tried to make India into an Islamic state. He created separate departments to enforce moral codes called "Muhtasib". He also prohibited drinking and cultivation and use of Bhang. He forbid music in Mughal court and dismissed royal astrologers & astronomers. He also discontinued the practice of Jharoka darshan and the celebration of Dussehra.
He destroyed many Hindu temples and banned construction of them. In 1679, he re-imposed Jiziya and pilgrimage tax. He was not tolerant towards other religions and also banned celebration of Muharram. He was against Sikhs & executed 9th Sikh Guru Teg Bahadur which resulted transformation of sikhs into warring community.
His religious policies turned everyone against him mainly Rajputs, Sikhs, Marathas, Jats & Satnamis. This became the very reason for the decline of the Mughal empire. After his death, Nadir shah looted Delhi & imprisoned the new Mughal emperor in 1739.
Akbar built Agra fort with red stones in Agra, Panch Mahal and Jama masjid with Buland darwaja at Fatehpur sikri. He also built the Humayun Tomb which is the precursor of Tajmahal in Delhi.
Jahangir built Akbar's tomb in Sikandara near Agra and Itimaddaulah Tomb in Agra. He also built the shalimar bagh in Srinagar.
Shahjaha built Red fort and Jama masjid in Delhi. He built Moti masjid in Agra and Nishat Bagh in Srinagar whereas he built Diwan-i-am and Diwan-i-Khas under Red Fort.
Aurangzeb built Pinjore garden in Lahore and Moti Masjid in Delhi.
Akbarnama was the main theme of Mughal paintings whereas Hamznama was the most important work of Mughal's time consisting of 1200 paintings. Tansen (From Gwalior) was a great musician in Akbar’s court.
Abul Fazal wrote Ain–i–Akbari and Akbarnama in the Persian Language. Abul Faizi converted Mahabharata into the Persian language. He was the leading poet in Akbar's court. Abdul Hamid Lahori wrote Padshah Nama. He was from Shahjaha’s Court. Inayat Khan wrote Shahjaha Naha. He was also from Shahjaha’s Court. Dara Shikoh was the eldest son of Shahjaha. He converted Bhagvat Gita & Upanishads into Persian.
Two new corps "Tobacco and Maize" were added during the 17th century. Potato and chili came in the 18th century. Ghee and oil were cheaper at that time while Salts and sugar were costly.

Share:







Comments
Waiting for your comments