Green Revolution in India
by Devender
0 3179
Green Revolution was an extraordinary expansion in the production of food grains (particularly wheat and rice) that brought about a huge part from the presentation into agricultural nations of new, high-yielding assortments, starting during the twentieth century.
Green Revolution in India
It was introduced in India to reduce the dependence of India on foreign countries for food grains. It was aimed at making India a self-dependent and self-sustained nation when it comes to food grains availability.
- Conditions that prevailed before the introduction of the Green revolution:
- To tackle this shortage problem, the government had to import a lot of food from foreign countries
- The food prices rose very high following the wars with China in 1962, with Pakistan in 1965, and the drought of 1965-66
- The output of agriculture fell down and the USA sent inferior quality seeds during a shortage of food, under PL-480 Scheme because of India’s stand on Vietnam & India’s denial of accepting an economic policy package
- The Indian government made economic self-reliance & food self-sufficiency their top priority due to the grim Scenario of the 1960s
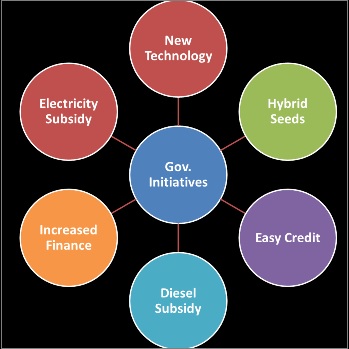
- Government’s positive initiative during Green Revolution Period:
- Farmers were provided public investment, institutional credit remunerative prices & new technologies
- The result of these efforts by the government was that the rate of increase in the gross irrigated area rose from 1 million hectares per annum to about 2.5 million hectares per annum during the pre-Green revolution in the 1970s
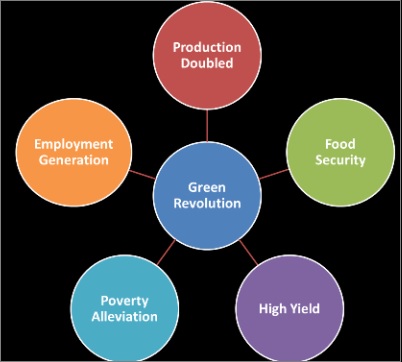
- Green Revolution's positive impact:
- It maintained the agricultural growth rates plus it generated a rapid increase in the marketable surplus of food grains
- India got freedom from the import of food for food security
- To get maximum results, small farmers applied more inputs per unit of land compared to large farmers
- Small farmers then became more confident & able
- Hence, they didn't sell their lands to large farmers in distress
- It increased the employment opportunities not only in the agriculture sector but also in nonagricultural rural & semi-urban employment through the development of agro-industries, transport industry, and other agriculturally allied sectors
- The income of the farmers increased which also brought the increase in demand for consumer durables like radios, watches, TVs, Sewing machines, etc.
- The stocks of food grains increased which helped government to launch employment generating and poverty alleviation programs in backward areas
- Green revolution also helped in decreasing poverty in rural areas by increasing food availability and decreasing the prices of food
- It also generated employment in the agricultural sector & agriculturally allied areas
- Green Revolution's negative impact:
- It rose the feeling of regionalism which divided the nation into developing and backward states
- To please the farming community in the Green Revolution belt, many politicians provided free electricity or subsidy on it to farmers which led to misuse of it
- It affected the overall Indian economy
Indian agriculture was only focused on institutional reforms and not on a technological base whereas the rise in population and huge outlays towards planned industrialization put a lot of pressure on the agriculture sector and the demand for food grains increased.
The government started investing in the agriculture sector even more and doubled the institutional finance in this sector from 1968 to 1973. The government set up the Agricultural price commission aiming to provide assure sustained remunerative prices to farmers.
The production of food grains rose significantly and by the 1980s, India didn't only become self-sufficient in food but also became able to export food to pay back the loans and to provide loans to other countries.
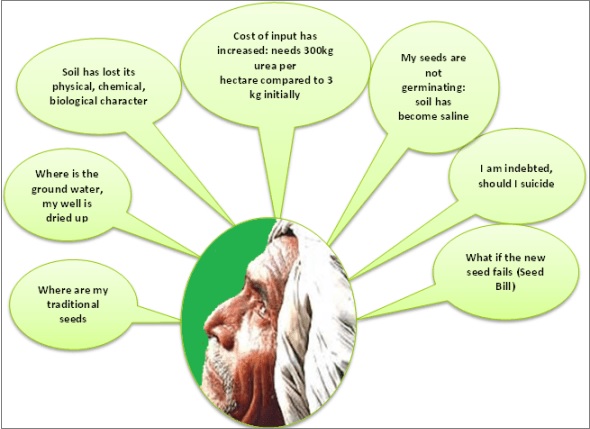
It led to excessive use of chemical fertilizers & pesticides and groundwater for irrigation. It also led to plateauing of the growth rates in areas like Punjab & Haryana. Tenants and sharecroppers were the only losers.

Share:





Comments
Waiting for your comments