Persian & Macedonian Invasion
by Devender
0 2640
During the rule of Bimbisara, Magadha kept on ascending in Northeast and Central-north in India. In the Northwest front of India, several small provinces Kamboja, Gandhara & Madra existed. These provinces didn't have any political unity and always fought with each other.
Persian Invasion
Cyprus was the Archaemadian ruler of Iran at that time. He took advantage of the political disunity of Kamboja, Gandhara & Madra and attacked the Northwest front of India in 550 BC. All the Indian tribes even Gandhar which were west of the Indus river submitted to his reign.
The grandson of Cyprus, Darius 1 conquered Indus valley and Punjab & Sindh i.e. entire North-western India. The successor of Darius was Xerxes who employed Indian infantry and cavalry in the war against Greece but got defeated which halted them to move forward in India. However, the Persians still had a great hold over India which was only slackened after the invasion of Alexander on India.
- Effects of Persian Invasion:
- Indo-Iranian trade and commerce started which became the main reason for Alexander's Invasion
- The use of Kharoshti script which was bought by Iran became famous in Northwest India
- Persian arts influence increased in India
Macedonian Invasion
Macedonian Invasion or otherwise known as Alexander's invasion of India happened in 327 BC after almost 200 years of the Persian Invasion. Alexander was able to control a minor part of Asia along with Iraq and Iran from where he marched into India. Alexander defeated Darius 3 in the battle of Arabela (330 BC) and hence, conquered the whole of Persia. The tremendous wealth of India, rich hereditary culture, and natural history attracted him to India.
He believed by capturing India he would have captured the eastern boundary of the world as on the eastern side of India only lies the sea. After his conquest of Iran, he marched in India through the Khyber pass and crossed Indus in 326 BC.
The ruler of Taxila, Ambhi submitted to Alexander willingly while Porus whose kingdom lay between Jhelum and Chenab refused to submit which brought the battle of Hydaspes.
- Battle of Hydaspes (Jhelum):
- Effect of Alexander's Invasion:
Porus had a huge army and he fought bravely against but that wasn't enough to get the victory. Alexander was impressed with the bravery of the Indian prince that's why he reinstated the prince back to the throne and made him his ally. After that, he marched to river Beas.
Alexander wanted to move further but the Greek soldiers refused due to war-weary, diseases, hot weather of India, and 10 years of continuous fighting. One of the prime reasons for refusing was the enormous power of Nandas of Magadha. So, Alexander divided its territories into 3 parts and placed them under the governance of Greek officials.
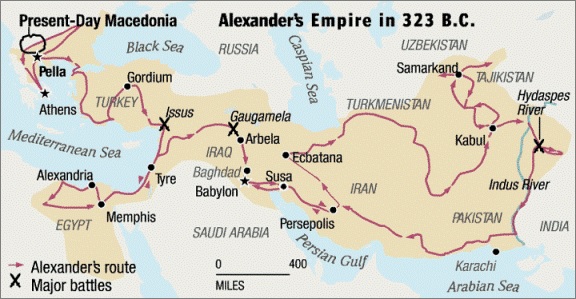
It was the first contact between India and Europe which increase trade and commerce between the two. It also increased the political unification of India.
Alexander's rule in the Indus valley was for a small time as the expansion of the Mauryan empire happened under Chandragupta Maurya.

Share:





Comments
Waiting for your comments