Gupta Empire
by Devender
0 2768
When the Kushan Empire was in ruins, Gupta Empire rose up. They ruled for over 200 years from 400 to 600 AD. It constituted major parts of UP & Bihar.
Gupta Empire
The Gupta empire's main center of power was at Prayag(Allahabad). Srigupta was known as the founder of the Gupta Dynasty. He was succeeded by Ghatochkacha and both of them were known as Maharaja.
- Chandragupta 1:
- Samundragupta:
- Chandragupta 2:
- Fall of Gupta Empire:
- The rise of Yashodharman in Malwa
- Invasion of Hunas from Central Asia
- Dissention within the royal family & weak rulers
- Gupta's Administration:
- Religion & Social Culture:
- Art & Culture:
- Literature:
- Kalidasa: Abhigyanshakuntalam, MalvikagnimitramVikramorvasiya, KumarsambhavaRaghuvamsa, Ritusamhara, Meghaduta
- Vishakadatta: Mudrarakshash & Devi – Chandraguptam
- Vishnusharma: Panchtantra stories
- Sudraka: Mrich – chakatika (Little clay art or toy cart)
- Amarsimha: Amarkosha (Lexicon in sanskrit)
- Dandin: Kavyadarsa & Desa – kumarcharita
- Science and Technology:
- Aryabhatta: Aryabhatiyam, Suryasidhhanta
- Varahmitra: Panch sidhhanta (5 astronomical system), Brihadsamhita, Brihadjataka (Astrology)
- Vagbhata: Ashtangasamgraha (Summary of 8 branches of Medicine)
He was the first one to be called Maharajadhiraja which meant Great king of kings. He is considered to be the founder of the Gupta dynasty because of his ascent. He was married to Lichchhavi princess which provided him with strength and prestige. His extensive quests are inscribed on the Mehrauli iron pillar.
He is known as the Napoleon of India and the greatest ruler of the Gupta dynasty. He was opposite to Ashoka and believed in military conquest. His conquests are mentioned on the inscriptions of the Allahabad pillar. It is the same pillar on which peace-loving Ashoka inscriptions can be found.
Samundragupta never tasted defeat and conquered most of India. He was a follower of Vaishnavism but he was tolerant of other religions too. He was an art & literature lover and self-proficient in music & poetry that is why he is also known as Kaviraja. He patronized many poets & scholars along with the famous Harisena.
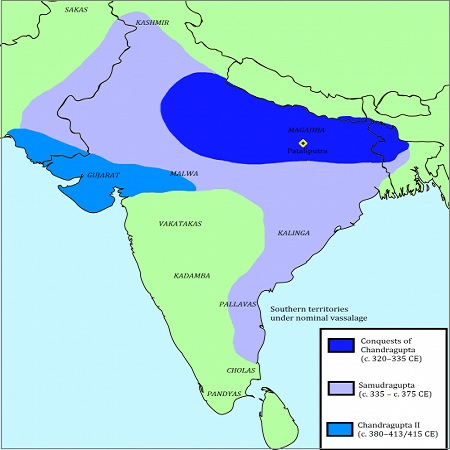
He was known as Chandragupta Vikramaditya and in his reign, the Gupta empire extended to new areas by either military quests or marriage alliances. He defeated shakas in Malwa & Gujarat and conquered western seaports. Ujjain became the second capital of Guptas after Prayag and his reign at Ujjain court saw numerous scholars including "Kalidasa & Amarsimha".
During his reign, the Chinese pilgrimage Fa-hsien/Fahien (399-414 AD) visited India. His exploits can be seen on the Qutub iron pillar in Delhi.
There were various reasons for the fall of the Gupta empire but the major ones were:
There was one other reason for the fall of the Guptas, the early Guptas followed Hinduism and supported other religions but the later Guptas turned to Buddhism.
Guptas assumed titles like parmeshwara, Maharajadhiraja & Paramabhattaraka which was unlike Mauryas, and the provinces under Guptas were known as Bhuktis & provincial governors as Uparikas. Kings used to maintain close interactions with provincial administration through officials known as Kumaramatyas and Ayuktas.
The provinces were further divided into districts called Vishayas under the charge of Vishayapati. There was a foreign affairs minister to look after any foreign affairs and they were known as Sandivigraha. Villagers were subjected to forced labor called Vishti for serving the royal army & officials.
Brahamanas were at the top and they used to receive a lot of gifts during the Guptas period. Brahamanism reigned supreme and it had 2 branches: Vaishnavism & Shaivism. However, Vaishnavism was more prevalent in this period. The Chinese pilgrimage, Fahien account tells about the decline of Buddhism in the Gangetic valley during this time but still, a few Buddhist monks like Vasubandhu were patronized by Gupta kings.
The Gupta period is known as the golden age of India in art, science, and literature. In this period, the Nagara & Dravidian styles of art evolved and the Delhi iron pillar, 7 ½ feet Buddha statue & Deogarh temple are the finest examples of Gupta art. Mural paintings of Ajanta, which mainly depicted life stories of Buddha as in Jtaka stories belong to this period and even paintings at Sigiria in Srilanka are influenced by Ajanta paintings.
Sanskrit became the primary language in the Guptas period and Ramayana & Mahabharata were compiled during this period. Some of the famous literature by famous poets are listed below:

Share:





Comments
Waiting for your comments