Savanna Climate (Sudan Type Climate) – Tropical Grasslands
by Devender
0 3676
The savanna or Sudan climate is a transitional type of climate and is found between the equatorial forests and trade wind hot deserts. It is called the Sudan climate as it is best developed in Sudan, where the dry & the wet climate are most distinct.
Savanna Climate (Sudan Type Climate) – Tropical Grasslands
It is confined within the tropics (Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn) and it covers a lot of parts of Africa (Kenya, Nigeria, Gambia) and large areas of Australia, South America (Brazilian highlands), as well as India. It is characterized by –
- An alternate & distinct hot, rainy season (from May to Sept)
- A cool, dry season (Oct to April) in N-Hemisphere & vice versa in S-Hemisphere
- This climate has a temperature range of 18 to 30 Degree C
- In winters, it is around 18 - 25 Degree C
- In summers, it is around 25 - 30 Degree C
- The annual precipitation is around 100 cm which is less than the tropical monsoon climate
- The length of wet and dry seasons differs with locality
- The prevailing winds of this region are trade winds
- These trade winds bring rain to the eastern coastal districts
- These winds reach the Guinea coast as dry dust-laden winds locally known as Harmattan which means the doctor
- They increase the rate of evaporation and provide a cooling effect at the Guinea coast
- These dry, dusty winds are also responsible for ruining the crops and causing fire
- They also stir up a thick dusty haze and hinder the inland river navigation
- The natural vegetation of Savanna Climate Region:
- These trees are deciduous and generally shed their leaves in the cool, dry season to avoid any excessive loss of water through transpiration
- Trees have big trunks to store water in order to survive through the drought
- Trees like Palms that cannot handle drought are located in the wettest areas near the rivers
- The roots reach down in search of water
- Short trees and low bushes are present in between the long grasses
- The savanna merges into thorny scrubs as rainfall decreases towards the deserts
- Savanna Animals and agriculture:
- Some tribes like the Masai of Kenya live here as pastoralists
- There are other tribes too like Hausa of Nigeria that lives here as settled cultivators
- This region has the greatest diversity of hoofed mammals
- The soil of the tropical grasslands is porous, with rapid drainage of water
- Therefore, most of the savanna areas have poor laterite soils
- This soil is not capable of supporting good crops unless the soil is properly conserved by manuring & weeding
- Savanna is known as a natural cattle country & many of its native people are herdsmen and pastoralists
- The cattle kept in large numbers for meat & milk
- Food crops - Maize, Millet, Corn, Bananas, Beans & Groundnuts
- Plantation crops - Cotton, Tobacco, Sugarcane, Coffee, Groundnuts, Oil palms & Tropical fruits
Same as the monsoon climate, the maximum temperature occurs in late spring to early summer before the rainy season. The daily temperature range is greater during the dry season and the annual temperature range increases towards the pole from the equatorial region. The length of the rainy season and annual total rainfall decreases from the equatorial region to the poles.
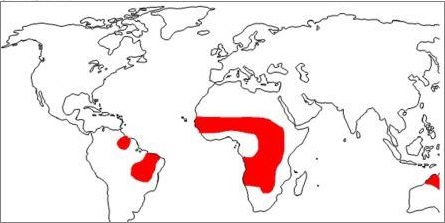
These winds are the strongest in summers but they get relatively dry by the time they reach the continental interiors or western coasts of the continent. That is why the region is dominated by scattered grasses & short trees. In West Africa, the N-E trade winds blow from the Sahara desert.
The savanna landscape is categorized by Tallgrass (6-8 feet) & short trees and is known as tropical grasslands. However, it is rather misleading as trees are also present along with the grasses. The trees grow best towards the equatorial humid latitudes or along the river banks. The decrease in the height and density of trees happens away from the equator.
Trees renew their foliage & flower in the rainy season and that is when the vegetative luxuriance is at its peak. However, the grasses lie resting during the long dry period and spring up in the rainy season. In the true savanna lands, the grass grows very tall and coarse up to 6 -12 feet in height. These grasses are known as Elephanta grass and grow in tufts with long roots.



Savanna is home to diverse varieties of wild animals, mainly in Africa. Most of the animal films are shot here. The tropical grassland animals include giraffes, zebras, buffaloes, kangaroos, mice, moles, gophers, ground squirrels, snakes, worms, termites, beetles, lions, leopards, hyenas, Zebu cattle, and elephants.
It has a very thin layer of humus that provides the vegetation with nutrients. The deterioration of soil fertility is because of the distinct wet & dry periods in this climate. The drainage of soil nutrients takes place during the rainy season as heavy rainfall causes leaching while during the dry season, the intense heating & evaporation dries up soils water.
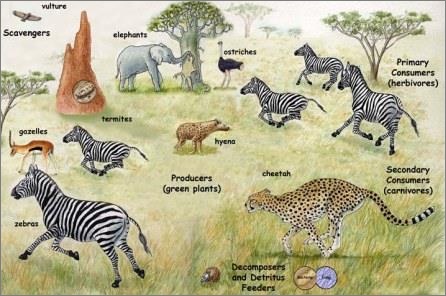
However, the settlements in central Africa, Northern Australia & Eastern Brazil have shown immense growth potential in food & plantation crops such as -

Share:








Comments
Waiting for your comments