Pointer to Pointer in C Language
0 1259
A pointer that stores the memory addresses of another pointer is called a Pointer to a Pointer.
pointer to pointer is also known as a double pointer.
double-pointer allows indirect access to a memory address.
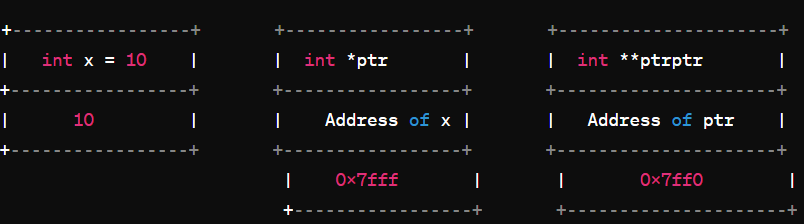 int x = 10: This line declares an integer variable x and initializes it with the value 10.
int *ptr: This line declares a pointer variable ptr of type int *, which means it can store the address of an integer variable.
int **ptrptr: This line declares a pointer to a pointer variable ptrptr of type int **, which means it can store the address of a pointer variable.
Address of x: The memory address where the variable x is stored. In this example, let's say x is stored at address 0x7fff.
Address of ptr: The memory address where the pointer variable ptr is stored. In this example, let's say ptr is stored at address 0x7ff0.
ptr stores the address of x: The pointer variable ptr holds the memory address of variable x (i.e., 0x7fff).
It points to the location where x is stored in memory.
ptrptr stores the address of ptr: The pointer to the pointer variable ptrptr holds the memory address of the pointer variable ptr (i.e., 0x7ff0).
It points to the location where ptr is stored in memory.
int x = 10: This line declares an integer variable x and initializes it with the value 10.
int *ptr: This line declares a pointer variable ptr of type int *, which means it can store the address of an integer variable.
int **ptrptr: This line declares a pointer to a pointer variable ptrptr of type int **, which means it can store the address of a pointer variable.
Address of x: The memory address where the variable x is stored. In this example, let's say x is stored at address 0x7fff.
Address of ptr: The memory address where the pointer variable ptr is stored. In this example, let's say ptr is stored at address 0x7ff0.
ptr stores the address of x: The pointer variable ptr holds the memory address of variable x (i.e., 0x7fff).
It points to the location where x is stored in memory.
ptrptr stores the address of ptr: The pointer to the pointer variable ptrptr holds the memory address of the pointer variable ptr (i.e., 0x7ff0).
It points to the location where ptr is stored in memory.
Syntax of Pointer to Pointer
Datatype**PointerToPointerVariableName;Example:
// Program of pointer to pointer in COutput:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int A = 12;
int *ptr = &A; // Pointer to an integer
int **ptr_to_ptr = &ptr; // Pointer to a pointer
printf("Value of A: %d\n", A);
printf("Value of A using pointer: %d\n", *ptr);
printf("Value of A using pointer to pointer: %d\n", **ptr_to_ptr);
return 0;
}
Value of A: 12
Value of A using pointer: 12
Value of A using pointer to pointer: 12

Share:








Comments
Waiting for your comments