Persistent MR Environments
0 258
📌 What are Persistent MR Environments?
Persistent MR Environments are mixed-reality spaces where virtual objects, anchors, and scene state persist across sessions, devices, and users. Instead of ephemeral overlays that disappear once an app closes, persistent MR keeps digital content anchored to real locations or world coordinates so that the experience continues later — with the same spatial relationships and shared history.🔗 Why persistence matters (real-world value)
Persistence transforms MR from a demo-level trick into a practical platform. Use cases include:- Training & simulations that resume exactly where the learner left off.
- Retail: product placements that remain in a store for multiple visits.
- Collaboration: teams annotating a physical space and returning to the same annotations later.
- Digital twins and long-term monitoring where objects represent real infrastructure states.
🧠Core building blocks of a persistent MR system
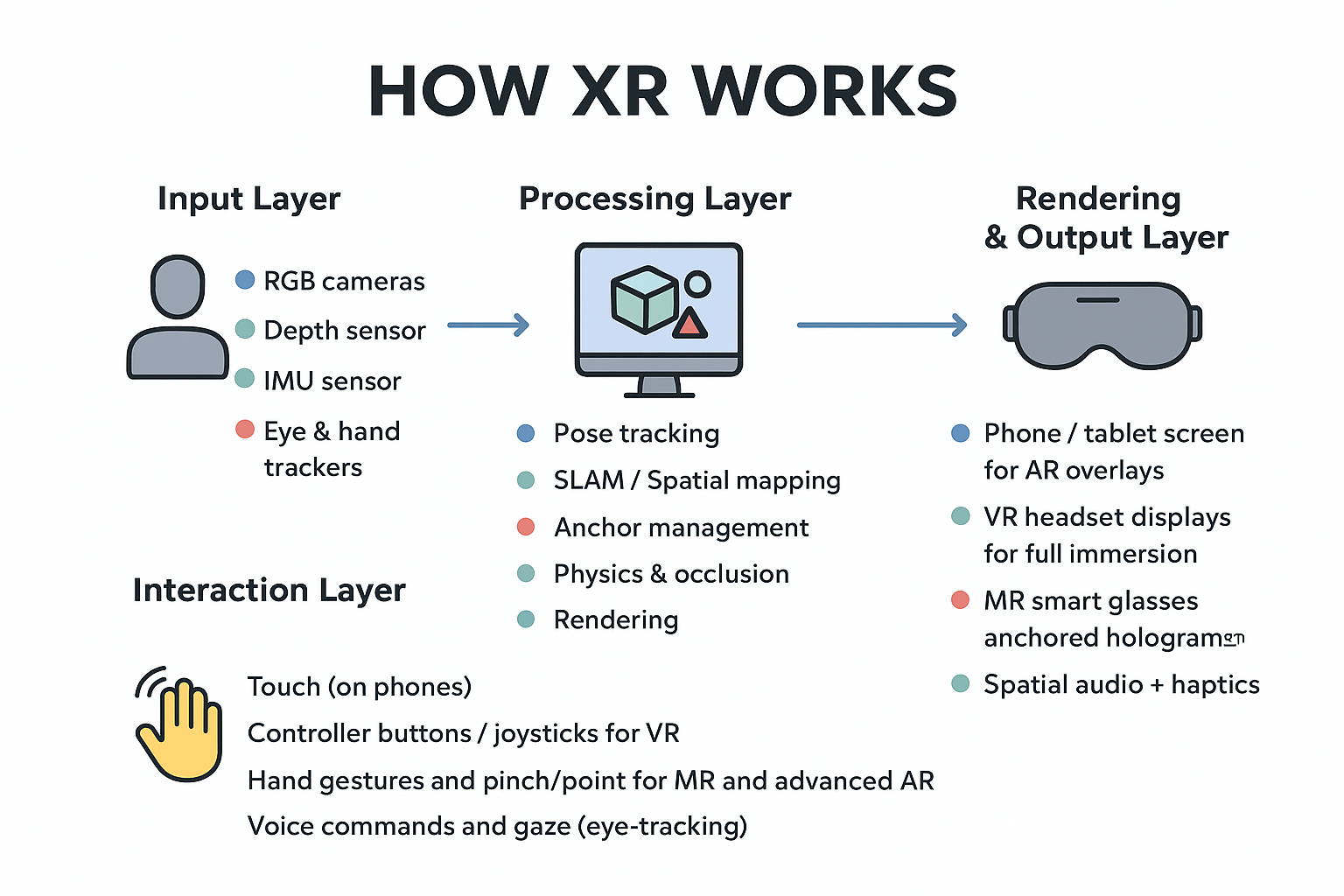
A robust persistent MR environment typically includes:- Spatial Anchors — stable references in the physical world (position + orientation).
- Serialization — saving object state (transform, metadata, timestamps).
- Cloud / Backend — authoritative store for anchors and scene state shared across clients.
- Relocalization — matching a device’s camera/SLAM map to a stored anchor so content reappears in-place.
- Access & Permissions — who can read/write anchors and when (multi-user coordination).
âš™ï¸ Typical architecture (high level)
Devices (AR headsets, phones) run local SLAM to create a coordinate frame. When the user places content, the app creates a spatial anchor and sends the anchor ID plus object state to a backend. Later, other devices request the anchor ID, relocalize to the anchor and fetch object state to reconstruct the scene.🧪 Quick example: A-Frame (WebXR) — store anchor data server-side
The example below shows a simple pattern: when a user places an object, store its transform to a backend. On load, fetch saved transforms and recreate objects. This is intentionally minimal — production needs authentication, conflict resolution, and robust relocalization.
<!-- index.html (A-Frame + minimal JS) -->
<html>
<head>
<script src="https://aframe.io/releases/1.4.0/aframe.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<a-scene embedded vr-mode-ui="enabled: false">
<a-entity id="camera" camera look-controls wasd-controls position="0 1.6 0"></a-entity>
</a-scene>
<script>
// PSEUDO: on place, POST transform to /api/anchors
async function placeObject(transform) {
await fetch('/api/anchors', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {'Content-Type':'application/json'},
body: JSON.stringify({id: crypto.randomUUID(), transform})
});
}
// On load, GET saved anchors and recreate
async function loadAnchors() {
const res = await fetch('/api/anchors');
const anchors = await res.json();
anchors.forEach(a => {
const el = document.createElement('a-box');
el.setAttribute('position', `${a.transform.x} ${a.transform.y} ${a.transform.z}`);
document.querySelector('a-scene').appendChild(el);
});
}
window.addEventListener('load', loadAnchors);
</script>
</body>
</html>
ðŸ› ï¸ Example: Unity / AR Foundation — saving and loading anchors (C#)
The C# snippet below sketches the flow: create an anchor, serialize its pose, and POST it to a backend. (In production you’d use robust anchor APIs — e.g., platform cloud anchors — and handle sessions/TTL.)
// AnchorManager.cs (sketch)
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.XR.ARFoundation;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
public class AnchorManager : MonoBehaviour {
public ARAnchorManager arAnchorManager;
private HttpClient http = new HttpClient();
public async Task CreateAndUploadAnchor(Pose pose) {
var anchor = arAnchorManager.AddAnchor(pose);
if (anchor == null) return;
var payload = JsonUtility.ToJson(new {
id = System.Guid.NewGuid().ToString(),
position = new { x = anchor.transform.position.x, y = anchor.transform.position.y, z = anchor.transform.position.z },
rotation = new { x = anchor.transform.rotation.x, y = anchor.transform.rotation.y, z = anchor.transform.rotation.z, w = anchor.transform.rotation.w }
});
await http.PostAsync("https://your-backend.example.com/anchors",
new StringContent(payload, Encoding.UTF8, "application/json"));
}
}
🔠Security, privacy & data management
Persistence raises new security considerations:- Encrypt anchor payloads in transit and at rest.
- Use access tokens and scopes — give read-only viewers limited access.
- Audit anchor creation/update and provide deletion tools (users must be able to remove anchored content).
- Respect privacy: anchored content tied to private spaces should not be globally discoverable.
🧩 Common challenges & how to mitigate them
Relocalization drift: different device SLAM maps can place anchors slightly differently. Use robust point-cloud matching, multiple anchor points, or semantic anchors (e.g., walls, corners) to improve alignment.Anchor lifecycle: decide TTL, refresh strategies, and housekeeping so stale anchors don’t clutter the world.
Network dependency: design for offline caching and graceful degradation (local-only fallbacks).
🚦 Best practices checklist
When building Persistent MR Environments, keep this checklist handy:- Use stable coordinate systems and store pose + confidence metrics.
- Version anchor schemas and keep backward compatibility in mind.
- Provide UX to show anchor ownership, timestamps, and sync status.
- Test relocalization in real-world lighting and clutter conditions.
- Plan for privacy, deletions, and moderation of persisted content.
🔠Future directions
As edge compute, 5G, and model-based SLAM improve, persistent MR will blend more naturally with the world: ephemeral UIs will evolve into contextual, always-present layers that respect place and time. Expect richer collaboration, live data overlays on infrastructure, and smarter anchors that include semantic metadata (what the anchor represents).🧾 Final thoughts / Conclusion ✨
Persistent MR Environments shift the promise of mixed reality from single-session demos to continuous, shared, and practical experiences. By combining reliable spatial anchors, secure backends, and thoughtful UX, you can create MR worlds that people return to — and that keep growing richer with each session. Start small (simple saved anchors + offline fallbacks), measure relocalization quality, and iterate toward a resilient persistent world.If you’re passionate about building a successful blogging website, check out this helpful guide at Coding Tag – How to Start a Successful Blog. It offers practical steps and expert tips to kickstart your blogging journey!
For dedicated UPSC exam preparation, we highly recommend visiting www.iasmania.com. It offers well-structured resources, current affairs, and subject-wise notes tailored specifically for aspirants. Start your journey today!

Share:



Comments
Waiting for your comments