XR in Manufacturing
0 281
ðŸ What does XR in Manufacturing really mean?
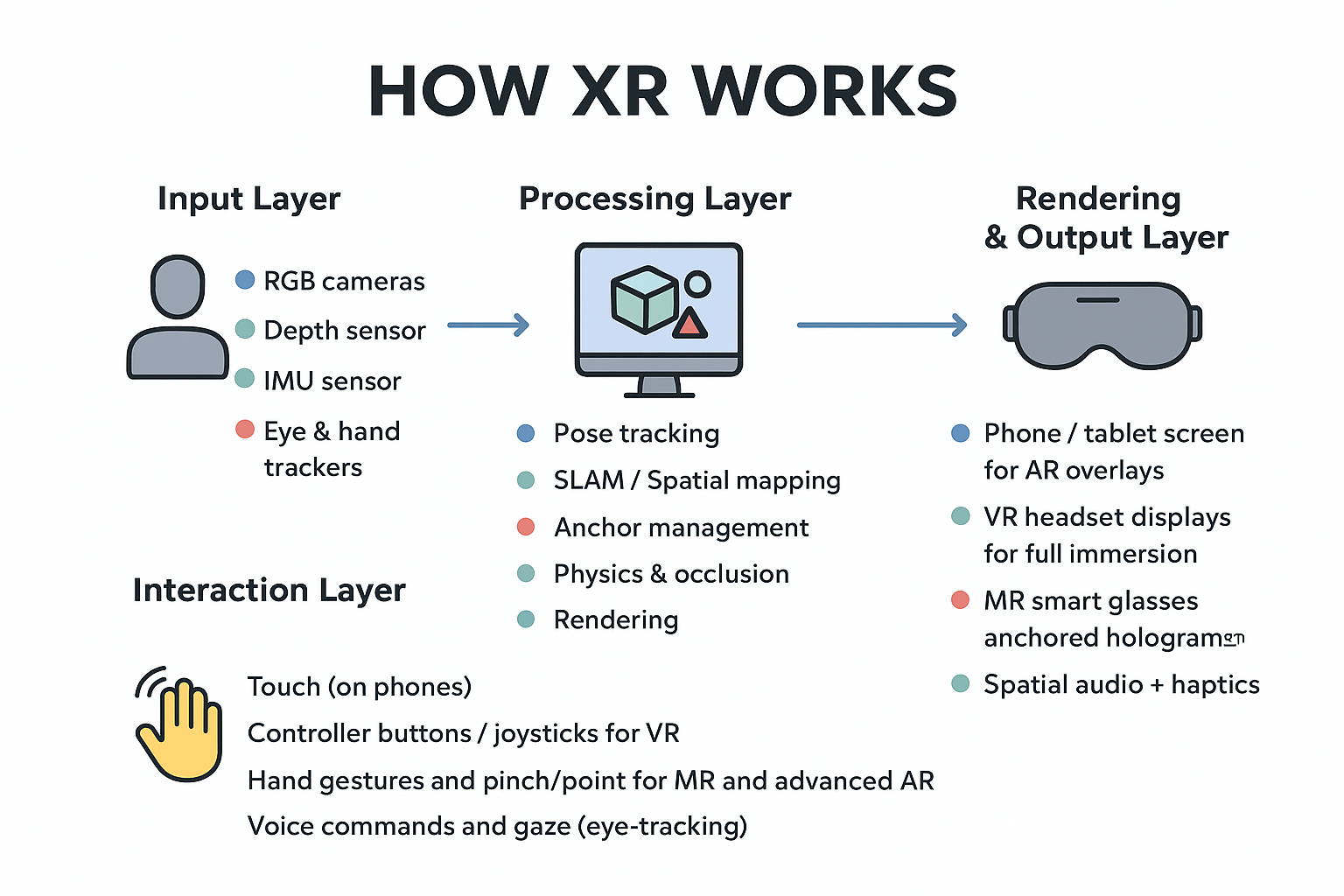
XR in Manufacturing refers to the practical use of Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality, and Mixed Reality inside industrial environments. Instead of relying only on manuals, screens, or classroom training, workers interact with spatial instructions, simulations, and real-time data layered directly onto machines and factory floors.🚀 Why manufacturing is adopting XR faster than other sectors
Manufacturing demands precision, speed, and safety. XR solves real problems here by reducing human error, shortening training cycles, and allowing experts to assist remotely. From assembly lines to maintenance bays, immersive guidance fits naturally into hands-on workflows.🧠Core use cases of XR in Manufacturing
- AR-guided assembly: step-by-step overlays directly on physical components
- VR training simulations: risk-free practice for complex or dangerous tasks
- Remote expert assistance: live annotations from off-site specialists
- Digital twins: real-time virtual replicas of machines and production lines
- Quality inspection: visual comparison between expected and actual builds
🧩 AR workflow example: guided assembly logic
Below is a simplified logic example showing how an AR system might progress through assembly steps based on task completion signals.
const steps = [
"Place motor housing",
"Insert bolts",
"Tighten bolts to torque spec",
"Attach sensor cable"
];
let currentStep = 0;
function nextStep() {
if (currentStep < steps.length) {
showOverlay(steps[currentStep]);
currentStep++;
} else {
showMessage("Assembly complete");
}
}
ðŸ› ï¸ VR training simulation flow
VR training in manufacturing focuses on muscle memory and decision-making. Simulations replicate machines, sounds, and failure scenarios so workers can learn without shutting down real equipment.
if (userAction === "incorrect") {
highlightError();
replayScenario();
} else {
increaseScore();
proceedToNextTask();
}
📡 Digital twins and real-time data sync
Digital twins connect physical machines with virtual models. Sensor data feeds into XR views, allowing engineers to visualize performance, temperature, vibration, or faults in real time. This dramatically improves predictive maintenance and root-cause analysis.🔒 Safety and compliance benefits
XR improves safety by training workers for rare but dangerous situations and guiding them during live operations. Hazard zones, emergency shutdowns, and compliance steps can be visually reinforced, reducing accidents and downtime.📊 Measuring impact and ROI
Manufacturers adopting XR often track metrics such as reduced training time, lower defect rates, faster maintenance resolution, and improved worker confidence. These measurable gains help justify scaling XR across facilities.âš ï¸ Challenges to plan for
- Device comfort for long factory shifts
- Integration with existing MES and ERP systems
- Content updates as machines evolve
- Change management and worker adoption
🔮 The future of XR in Manufacturing
As headsets become lighter and AI integrates with XR, manufacturing environments will gain adaptive instructions, automated error detection, and smarter digital twins. XR will move from being a support tool to a core layer of industrial operations.🧾 Final thoughts / Conclusion ✨
XR in Manufacturing is no longer experimental — it’s a productivity multiplier. When implemented with clear goals, ergonomic design, and measurable outcomes, XR helps factories train faster, operate safer, and innovate smarter in an increasingly competitive industrial landscape.If you’re passionate about building a successful blogging website, check out this helpful guide at Coding Tag – How to Start a Successful Blog. It offers practical steps and expert tips to kickstart your blogging journey!
For dedicated UPSC exam preparation, we highly recommend visiting www.iasmania.com. It offers well-structured resources, current affairs, and subject-wise notes tailored specifically for aspirants. Start your journey today!

Share:



Comments
Waiting for your comments